Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection and prompt treatment of tick-borne diseases are crucial for successful recovery and preventing complications. If you develop symptoms after a tick bite or spending time in tick-prone areas, seek medical attention promptly.

Bull's-eye rash - early Lyme disease symptom
Image: Wikimedia Commons (CDC, Public Domain)
General Treatment Principles
- Early Treatment: Most tick-borne diseases respond best to early treatment
- Appropriate Antibiotics: The choice of antibiotic depends on the specific disease
- Complete Treatment: It's important to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed
- Follow-up Care: Some diseases may require follow-up monitoring
Treatment by Disease
Lyme Disease
Lyme disease is typically treated with antibiotics:
- Early Stage: Oral antibiotics such as doxycycline, amoxicillin, or cefuroxime for 10-21 days
- Later Stage: May require longer courses of antibiotics or intravenous antibiotics for severe cases
- Post-Treatment: Most people recover completely with appropriate treatment, though some may experience lingering symptoms
Note: In some cases, a single dose of doxycycline may be prescribed as prophylaxis after a tick bite in high-risk areas, but this should be discussed with a healthcare provider.

Deer tick (Ixodes scapularis) - Lyme disease vector
Image: Wikimedia Commons (CDC, Public Domain)
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF)
RMSF requires prompt treatment with doxycycline:
- Treatment should begin as soon as RMSF is suspected, even before test results are available
- Doxycycline is the treatment of choice for all ages, including children
- Early treatment significantly improves outcomes
- Delayed treatment can lead to severe complications or death
Anaplasmosis
Anaplasmosis is treated with doxycycline:
- Oral doxycycline is typically effective
- Treatment duration is usually 10-14 days
- Severe cases may require intravenous antibiotics
Babesiosis
Babesiosis treatment depends on severity:
- Mild Cases: Combination of atovaquone and azithromycin
- Severe Cases: Combination of clindamycin and quinine
- Treatment duration is typically 7-10 days
- Severe cases may require hospitalization
Ehrlichiosis
Ehrlichiosis is treated with doxycycline:
- Oral doxycycline for 10-14 days
- Severe cases may require intravenous antibiotics
- Early treatment is important for best outcomes
When to Seek Medical Attention
Seek medical attention if you experience:
- Symptoms after a known tick bite
- Fever, chills, or flu-like symptoms after spending time in tick-prone areas
- A rash, especially a "bull's-eye" rash (erythema migrans)
- Severe headache or neck stiffness
- Joint pain or swelling
- Neurological symptoms
- Any concerns about a tick bite
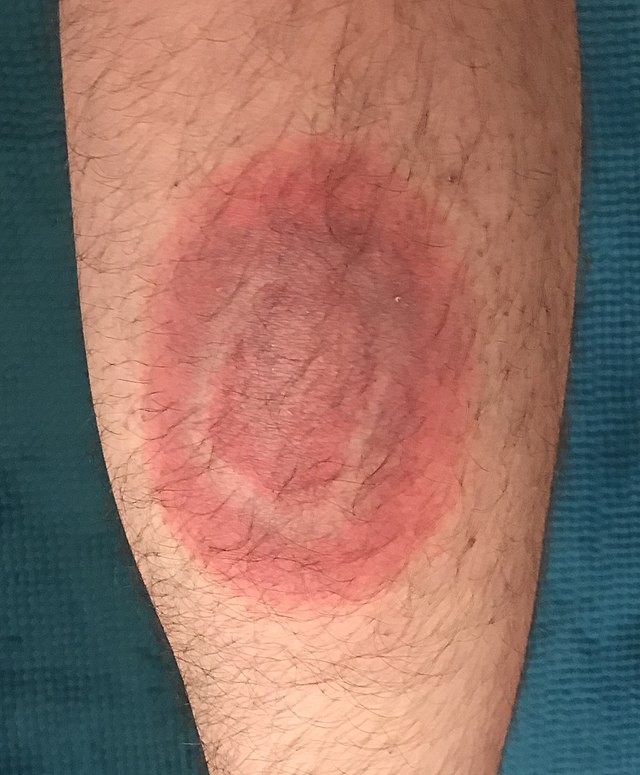
Bull's-eye rash - seek medical attention
Image: Wikimedia Commons (CDC, Public Domain)
Diagnostic Testing

Engorged tick specimen for testing
Image: Wikimedia Commons (CC BY 2.0)
Diagnosis of tick-borne diseases may involve:
- Clinical Evaluation: Assessment of symptoms and history of tick exposure
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests to detect antibodies or the presence of pathogens
- Tick Testing: In some cases, the tick itself may be tested for pathogens
Important: Early treatment may begin before test results are available, especially for diseases like RMSF where early treatment is critical.
Prevention of Complications
Early treatment helps prevent complications such as:
- Chronic symptoms
- Joint damage
- Neurological problems
- Cardiac complications
- Severe illness requiring hospitalization
Post-Treatment Monitoring
After treatment, your healthcare provider may recommend:
- Follow-up visits to monitor recovery
- Additional testing if symptoms persist
- Monitoring for potential complications
- Lifestyle modifications if needed
Important Considerations
- Complete the Full Course: Always complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if you start feeling better
- Follow Medical Advice: Follow your healthcare provider's instructions carefully
- Report Side Effects: Report any side effects or concerns to your healthcare provider
- Prevent Future Bites: Continue to take preventive measures to avoid future tick bites
Disclaimer
This information is for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.